Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
3. Biological Psychology
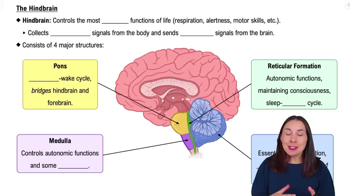
The Hindbrain
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Which area of the brain influences sleep and dreaming?
A
Pons
B
Reticular formation
C
Medulla
D
Cerebellum
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that the brain is composed of various structures, each responsible for different functions, including sleep and dreaming.
Identify the brainstem as a critical area involved in regulating sleep. The brainstem includes structures such as the pons, medulla, and reticular formation.
Recognize that the pons is a part of the brainstem that plays a significant role in regulating sleep cycles and is particularly involved in REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, which is associated with dreaming.
Consider the reticular formation, which is a network of neurons located in the brainstem that is crucial for maintaining arousal and consciousness, thus influencing sleep-wake cycles.
Differentiate the roles of the medulla and cerebellum. The medulla is primarily involved in autonomic functions like breathing and heart rate, while the cerebellum is involved in motor control, neither of which are directly responsible for sleep and dreaming.

 5:18m
5:18mWatch next
Master The Hindbrain with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice



![[Psychology] The Nervous System #04: The Hindbrain, Its Structures And Its Functions](https://img.youtube.com/vi/x2g-HpxLtDw/mqdefault.jpg)