Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
1. Introduction to Psychology
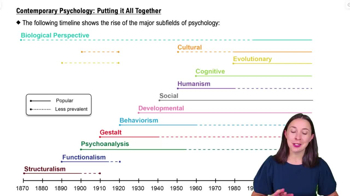
Contemporary Psychology: Putting it All Together
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Pavlov's work with learning in dogs focused on the concept of
A
conditioning.
B
shaping.
C
framing.
D
functionalism.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the context of the problem: The question refers to Pavlov's work, which is a foundational study in the field of psychology, specifically related to learning processes in animals.
Identify the key concept: Pavlov is best known for his research on classical conditioning, which involves learning through association.
Differentiate between the options: Conditioning refers to the process of learning associations between environmental events and behavioral responses. Shaping involves reinforcing successive approximations of a desired behavior. Framing is related to how information is presented to influence perception. Functionalism is a psychological philosophy that considers mental life and behavior in terms of active adaptation to the person's environment.
Focus on the relevant concept: Pavlov's experiments with dogs, where he paired a neutral stimulus (like a bell) with an unconditioned stimulus (like food) to produce a conditioned response (salivation), exemplify classical conditioning.
Conclude with the correct concept: Based on the understanding of Pavlov's work, the correct answer is 'conditioning,' as it directly relates to the process he studied and demonstrated through his experiments with dogs.

 4:54m
4:54mWatch next
Master Contemporary Psychology with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice