Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
4. Sensation and Perception
Visual Anatomy
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
_____ is due to the lack of functioning cones.
A
Monochrome color blindness
B
Deuteranopia
C
Protanopia
D
Tritanopia
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
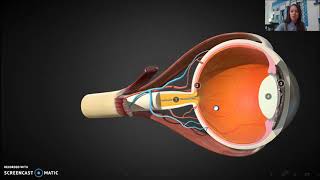
Begin by understanding the role of cones in the human eye. Cones are photoreceptor cells responsible for color vision. They are sensitive to different wavelengths of light, allowing us to perceive a range of colors.
Recognize that color blindness occurs when one or more types of cones are not functioning properly. This can lead to difficulty in distinguishing certain colors.
Identify the types of color blindness: Monochrome color blindness, Deuteranopia, Protanopia, and Tritanopia. Each type is associated with the dysfunction of specific cones.
Monochrome color blindness is due to the lack of functioning cones altogether, resulting in the inability to perceive any color, only shades of gray.
Deuteranopia, Protanopia, and Tritanopia are specific types of color blindness related to the dysfunction of green, red, and blue cones respectively. Understand that these conditions affect the perception of specific colors rather than all colors.

 3:08m
3:08mWatch next
Master Anatomy of the Eye with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















![The Human Eye & Color Blindness [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 3] (3.3)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Mwq23JTBnN0/mqdefault.jpg)







![The Process Of Smelling & Tasting [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 6] (3.6)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/vIQf0QAJFQA/mqdefault.jpg)




![Sensation of Touch, Layers of Skin & Pain [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 7] (3.7)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/sjbg9pf9Cj8/mqdefault.jpg)























![Factors affecting perception - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ot4AjaQUo3Y/mqdefault.jpg)
![Social & Cognitive Factors In Learning [AP Psychology Unit 4 Topic 4] (4.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Z1NIcVXplFk/mqdefault.jpg)