Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
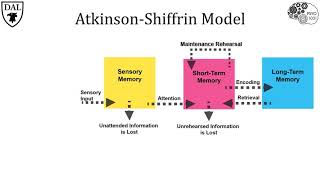
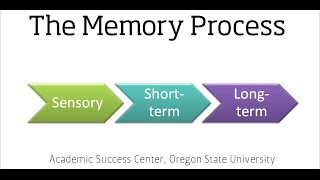
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Chad and Jeremy decide to train together to participate in a triathlon. Jeremy is doing it because he likes the challenge, but Chad is only doing it because he wants to win the prize money. Chad is being motivated by a(n) _____ drive.
A
affiliative
B
secondary
C
tertiary
D
primary
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of 'drive' in psychology, which refers to an internal state that motivates behavior towards a goal.
Identify the types of drives: primary drives are biological needs (e.g., hunger, thirst), while secondary drives are learned through experience and are not directly related to biological needs.
Recognize that Chad's motivation is not based on a biological need but rather on an external reward (prize money), which is a learned or acquired motivation.
Differentiate between primary and secondary drives: primary drives are innate, while secondary drives are associated with external incentives or rewards.
Conclude that Chad is motivated by a secondary drive, as his motivation is based on the desire for an external reward rather than an innate biological need.

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)












































![The Girl With The Three-Minute Memory (Amnesia Documentary) | Real Stories [4k]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZeiMhUlipTk/mqdefault.jpg)