Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
1. Introduction to Psychology
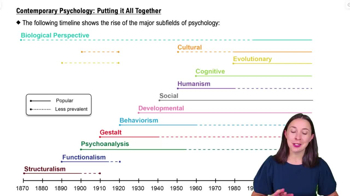
Contemporary Psychology: Putting it All Together
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Mary Cover Jones achieved counterconditioning with 'Little Peter' by using
A
loud noises.
B
toys.
C
verbal praise.
D
food.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of counterconditioning: Counterconditioning is a behavioral technique used to replace an undesirable response to a stimulus with a desirable one by associating the stimulus with a positive experience.
Identify the subject of the experiment: 'Little Peter' was a child who exhibited fear responses, similar to 'Little Albert' in earlier experiments.
Recognize the method used by Mary Cover Jones: She aimed to reduce Peter's fear responses by associating the feared stimulus with a positive experience.
Consider the options provided: loud noises, toys, verbal praise, and food. Each option represents a potential positive experience that could be used in counterconditioning.
Determine the most effective positive experience: Food is often used in counterconditioning because it is a primary reinforcer that can effectively create positive associations, leading to a reduction in fear responses.

 4:54m
4:54mWatch next
Master Contemporary Psychology with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice