Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
3. Biological Psychology
Organization of the Brain
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
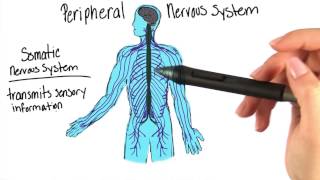
The nerves carrying messages from the central nervous system (CNS) to the voluntary muscles comprise the
A
sensory pathway.
B
motor pathway.
C
autonomic nervous system.
D
parasympathetic division.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by understanding the role of the central nervous system (CNS) in processing and sending out information to the body.
Recognize that the CNS communicates with different parts of the body through various pathways, each serving distinct functions.
Identify the sensory pathway as the route that carries information from sensory receptors to the CNS, not from the CNS to muscles.
Understand that the motor pathway is responsible for carrying messages from the CNS to voluntary muscles, enabling movement.
Differentiate between the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions, and the parasympathetic division, which is part of the autonomic system responsible for 'rest and digest' activities.

 2:26m
2:26mWatch next
Master Organization of the Brain with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice







![[Psychology] The Nervous System #03: The Central Nervous System And Its Basic Structures](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IALKGhUXr1s/mqdefault.jpg)



![[Psychology] The Nervous System #07: The Peripheral Nervous System](https://img.youtube.com/vi/E2hYzBUj9K0/mqdefault.jpg)