Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
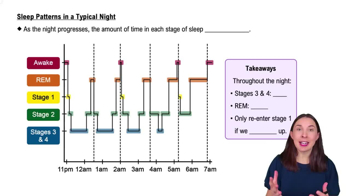
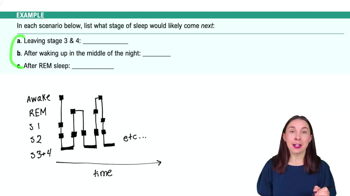
5. Consciousness and Sleep
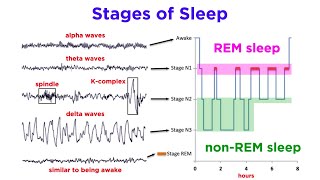
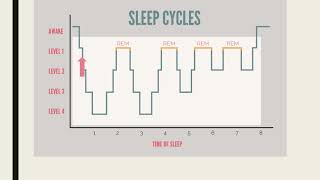
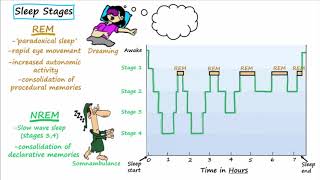
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Insomnia can be helped by
A
using sleeping pills.
B
dealing with anxieties directly before going to bed.
C
watching TV in bed.
D
going to bed only when sleepy.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the nature of insomnia: Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and not being able to go back to sleep.
Identify the ineffective strategies: Recognize that using sleeping pills, dealing with anxieties directly before bed, and watching TV in bed are not effective long-term solutions for insomnia.
Explore the concept of sleep hygiene: Sleep hygiene involves practices that promote regular, restful sleep, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a comfortable sleep environment.
Consider the principle of stimulus control: This principle suggests that the bed should be associated with sleep only, which means going to bed only when sleepy and avoiding activities like watching TV in bed.
Apply the correct strategy: To improve sleep quality, go to bed only when you feel sleepy, which helps strengthen the association between bed and sleep, thereby reducing insomnia symptoms.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)