Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
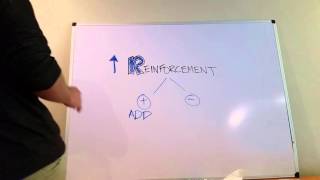
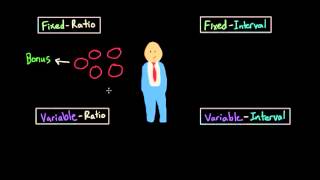
6. Learning
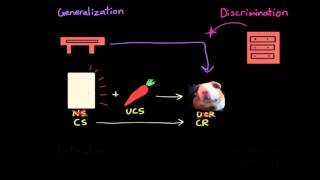
Classical Conditioning
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
The response that is given to the conditioned stimulus is not usually quite as strong as the original unconditioned response
A
because it is a completely different response.
B
but it is essentially the same response.
C
and it is an opposite response.
D
and it is difficult to predict whether it will be a similar or different response.

 3:29m
3:29mWatch next
Master Introduction to Classical Conditioning with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

















![Visual Illusions - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/7GJJXLiN4Ug/mqdefault.jpg)


























![Classical Conditioning [cc]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/cP5lCleK-PM/mqdefault.jpg)












































































































![3.22. Tardive Dystonia Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation - Dystonias [Spring Video Atlas]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ayPFIpXhoWY/mqdefault.jpg)