Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
6. Learning
Classical Conditioning
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Which of the following statements are accurate?
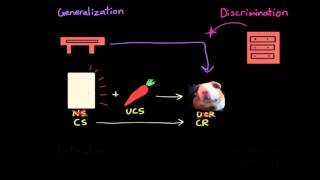
I) A cat runs to the kitchen every time they hear kibble being poured. Over time, the also begin to run to the kitchen anytime someone pours cereal. This is an example of stimulus generalization.
II) As stimulus generalization decreases, stimulus discrimination also decreases.
III) In stimulus discrimination, a similar stimulus will not elicit the conditioned response.
A
I & II.
B
II & III.
C
I & III.
D
I, II, & III
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the concept of stimulus generalization. It occurs when a conditioned response is elicited by stimuli that are similar to the conditioned stimulus. In the example, the cat runs to the kitchen when it hears kibble being poured, and over time, it also runs when cereal is poured. This is stimulus generalization because the cat responds to a similar stimulus (cereal pouring) in the same way it responds to the original stimulus (kibble pouring).
Step 2: Analyze statement I. It describes a scenario where a cat generalizes its response to a similar stimulus. This aligns with the definition of stimulus generalization, making statement I accurate.
Step 3: Understand the concept of stimulus discrimination. It is the ability to differentiate between the conditioned stimulus and other similar stimuli, leading to a response only to the conditioned stimulus.
Step 4: Analyze statement II. It suggests that as stimulus generalization decreases, stimulus discrimination also decreases. However, typically, as generalization decreases, discrimination increases because the subject learns to differentiate between stimuli.
Step 5: Analyze statement III. It states that in stimulus discrimination, a similar stimulus will not elicit the conditioned response. This is accurate because discrimination involves responding only to the specific conditioned stimulus and not to similar ones.

 3:29m
3:29mWatch next
Master Introduction to Classical Conditioning with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

















![Visual Illusions - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/7GJJXLiN4Ug/mqdefault.jpg)


























![Classical Conditioning [cc]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/cP5lCleK-PM/mqdefault.jpg)












































































































![3.22. Tardive Dystonia Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation - Dystonias [Spring Video Atlas]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ayPFIpXhoWY/mqdefault.jpg)