Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
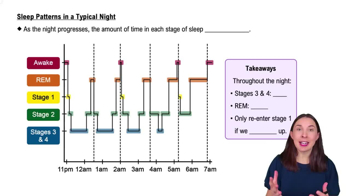
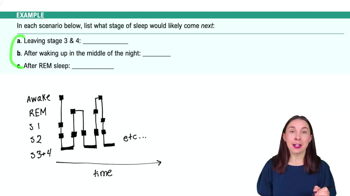
5. Consciousness and Sleep
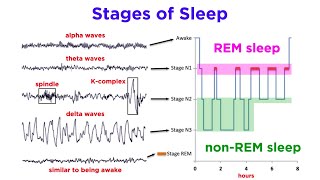
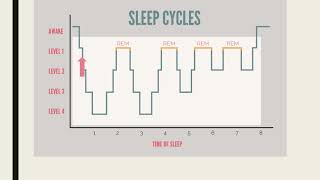
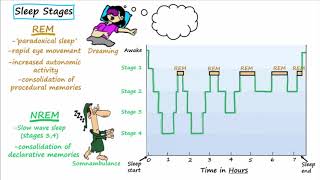
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
One of the earliest approaches to motivation focused on
A
the need for achievement.
B
biologically determined patterns of behavior.
C
universal needs that help people gain a complete sense of self.
D
performance and mastery goals.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by understanding the concept of motivation in psychology, which refers to the processes that initiate, guide, and maintain goal-oriented behaviors.
Explore the 'need for achievement' as a specific type of motivation, which is the drive to excel, achieve in relation to a set of standards, and strive to succeed.
Consider the historical context of motivation theories, such as the instinct theory, which suggests that certain behaviors are biologically determined and innate.
Examine the concept of 'universal needs' in the context of self-determination theory, which posits that people have inherent psychological needs that are essential for psychological growth and well-being.
Differentiate between 'performance goals' and 'mastery goals' in achievement motivation, where performance goals focus on demonstrating ability relative to others, and mastery goals focus on developing competence and understanding.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)