Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
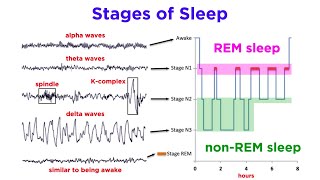
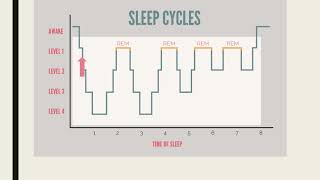
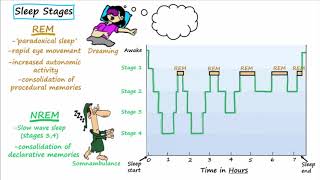
5. Consciousness and Sleep
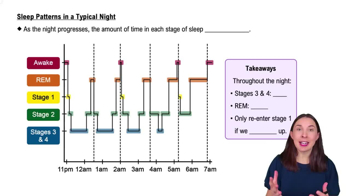
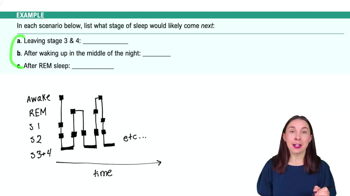
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Predators such as lions sleep _____ their prey, the gazelle.
A
fewer hours per day than
B
more hours per day than
C
the same number of hours per day as
D
on the same schedule a
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Consider the biological and evolutionary reasons for sleep patterns in predators and prey. Predators like lions have different energy needs and risks compared to prey animals like gazelles.
Understand that predators often have the luxury of sleeping more because they are at the top of the food chain and face fewer threats from other animals.
Recognize that prey animals, such as gazelles, need to remain vigilant and alert to avoid predators, which often results in them sleeping less.
Analyze the ecological and behavioral adaptations that influence sleep duration, such as the need for energy conservation and the balance between hunting and resting for predators.
Conclude that due to these factors, predators like lions typically sleep more hours per day than their prey, such as gazelles, as they do not need to be as alert to potential threats.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)