Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
3. Biological Psychology
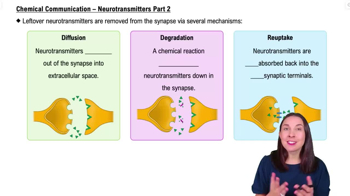
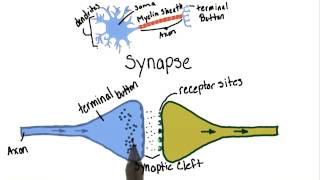
Communication in the Nervous System
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
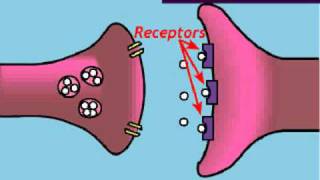
What is the role of ion channels in a neuron?
A
To allow vital nutrients in and out of the cell.
B
To allow for the movement of ions in and out of the cell.
C
To create an equal distribution of sodium and potassium on each side of the cell membrane.
D
To protect the neuron from invading pathogens.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
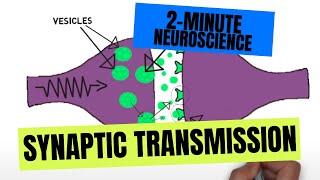
Understand that neurons are specialized cells in the nervous system responsible for transmitting information throughout the body.
Recognize that ion channels are protein structures embedded in the cell membrane of neurons, which play a crucial role in the neuron's ability to transmit signals.
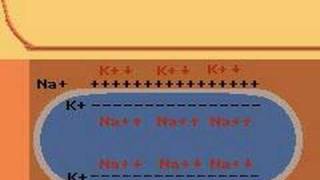
Ion channels allow specific ions, such as sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca2+), and chloride (Cl-), to move in and out of the neuron, which is essential for generating electrical signals known as action potentials.
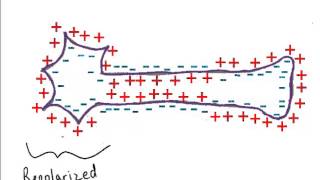
The movement of ions through these channels is critical for maintaining the neuron's resting membrane potential and for the depolarization and repolarization phases of the action potential.
Ion channels do not directly allow nutrients in and out of the cell, nor do they create an equal distribution of sodium and potassium; instead, they facilitate the selective movement of ions, which is vital for neuronal communication.

 1:20m
1:20mWatch next
Master Electrochemical Communication with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice