Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
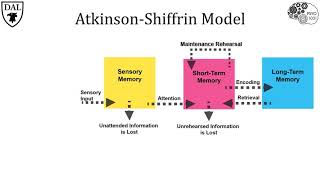
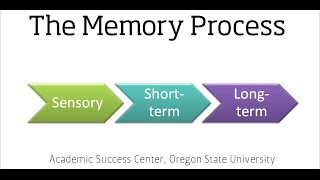
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
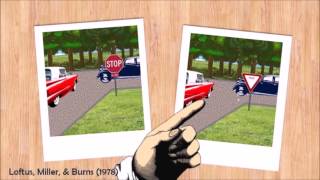
Namiko was in a study room during which he was shown a photo of a man with straight hair. Later, he was asked if he noticed the man's curly hair. Namiko was then convinced that the man in the photo had curly hair. This is an example of
A
the misinformation effect.
B
false-memory syndrome.
C
the curve of forgetting.
D
retrograde amnesia.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the key elements of the scenario: Namiko was shown a photo of a man with straight hair, but later believed the man had curly hair.
Understand the concept of the misinformation effect: This occurs when a person's memory of an event is altered by misleading information presented after the event.
Consider how the misinformation effect applies: Namiko's memory was influenced by the suggestion that the man had curly hair, leading to a false memory.
Differentiate from other concepts: False-memory syndrome involves larger, more complex false memories, while the curve of forgetting and retrograde amnesia relate to memory decay and loss, not alteration.
Conclude that the scenario is an example of the misinformation effect, as Namiko's memory was changed by misleading information.

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)












































![The Girl With The Three-Minute Memory (Amnesia Documentary) | Real Stories [4k]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZeiMhUlipTk/mqdefault.jpg)