Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
3. Biological Psychology
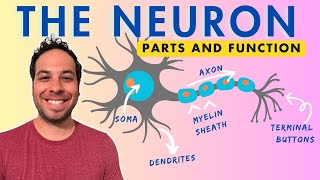
Cells of the Nervous System
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Myelin is not continuous for the length of the axon. What structures are formed by the gaps in myelin?
A
Dendritic terminals.
B
Axon terminals.
C
Nodes of Ranvier.
D
Glial gaps.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the role of myelin in the nervous system: Myelin is a fatty substance that wraps around the axon of a neuron, providing insulation and increasing the speed of electrical signal transmission.
Recognize that myelin is not continuous along the axon: There are periodic interruptions in the myelin sheath along the axon.
Identify the structures formed by these gaps: These interruptions are known as the Nodes of Ranvier.
Learn the function of the Nodes of Ranvier: They are crucial for the process of saltatory conduction, where the action potential jumps from one node to the next, speeding up neural communication.
Differentiate between the options provided: Dendritic terminals and axon terminals are different parts of the neuron, and glial gaps are not a recognized term in this context. The correct answer is Nodes of Ranvier.

 1:57m
1:57mWatch next
Master Neurons vs. Glial Cells with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice