Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
3. Biological Psychology
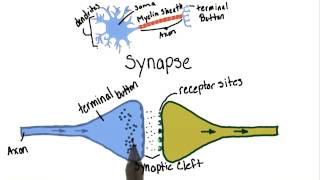
Communication in the Nervous System
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
An _____ is a chemical substance that mimics or enhances the effects of a neurotransmitter.
A
excitatory neurotransmitter
B
inhibitory neurotransmitter
C
antagonist
D
agonist
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
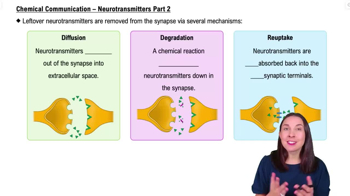
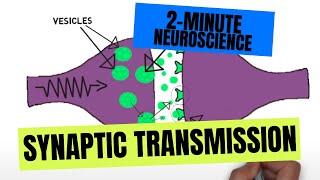
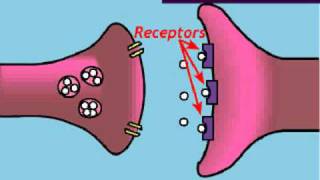
Understand the role of neurotransmitters: Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals across a chemical synapse, such as between a neuron and a muscle cell or another neuron.
Differentiate between types of neurotransmitters: Excitatory neurotransmitters promote the generation of an electrical signal in the receiving neuron, while inhibitory neurotransmitters prevent it.
Define an agonist: An agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor and activates the receptor to produce a biological response. It mimics or enhances the effects of a neurotransmitter.
Contrast with an antagonist: An antagonist is a substance that binds to a receptor but does not activate it, thereby blocking or dampening a biological response.
Apply the concept: In the context of the problem, identify that an agonist is the chemical substance that mimics or enhances the effects of a neurotransmitter, making it the correct answer.

 1:20m
1:20mWatch next
Master Electrochemical Communication with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice