Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
5. Consciousness and Sleep
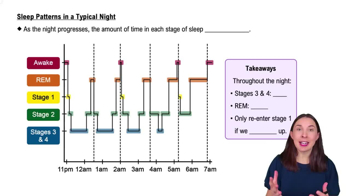
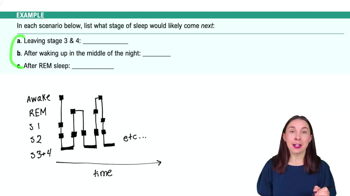
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
The heart rate slows, breathing becomes more shallow and irregular, and an EEG would show the first signs of sleep spindles in _____ sleep.
A
N1
B
N2
C
N3
D
REM
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
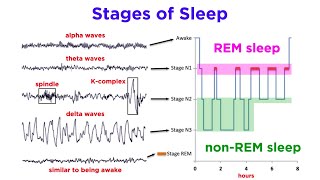
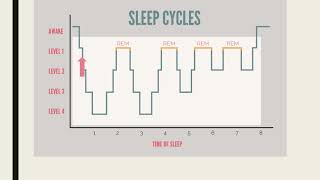
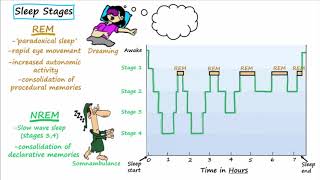
Begin by understanding the stages of sleep. Sleep is typically divided into non-REM (NREM) and REM sleep, with NREM further divided into stages N1, N2, and N3.
Recognize that N1 is the lightest stage of sleep, where a person can be easily awakened. It is characterized by slow eye movements and reduced muscle activity.
Identify N2 as the stage where sleep spindles first appear. Sleep spindles are bursts of oscillatory brain activity visible on an EEG, indicating a deeper sleep than N1.
Understand that N3 is the deepest stage of NREM sleep, often referred to as slow-wave sleep, characterized by delta waves on an EEG.
REM sleep is distinct from NREM stages, characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreams. It does not feature sleep spindles.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)