Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
3. Biological Psychology
Organization of the Brain
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
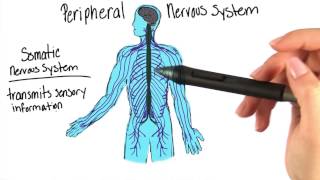
After a stressful situation, the parasympathetic division allows the body to
A
run from danger.
B
put back the energy it burned.
C
react quickly
D
suspend digestion.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the role of the parasympathetic nervous system: It is part of the autonomic nervous system responsible for 'rest and digest' functions, which help the body conserve energy and recover after stress.
Recognize the contrast with the sympathetic nervous system: The sympathetic division is responsible for 'fight or flight' responses, preparing the body to react quickly to danger by increasing heart rate, suspending digestion, and releasing energy.
Identify the function of the parasympathetic division after stress: It works to restore the body to a state of calm by slowing the heart rate, resuming digestion, and conserving energy.
Consider the options provided: 'run from danger' aligns with sympathetic activity, 'react quickly' is also sympathetic, and 'suspend digestion' is a sympathetic response.
Conclude that the parasympathetic division's role is to 'put back the energy it burned,' as it helps the body recover and conserve energy after a stressful event.

 2:26m
2:26mWatch next
Master Organization of the Brain with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice







![[Psychology] The Nervous System #03: The Central Nervous System And Its Basic Structures](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IALKGhUXr1s/mqdefault.jpg)



![[Psychology] The Nervous System #07: The Peripheral Nervous System](https://img.youtube.com/vi/E2hYzBUj9K0/mqdefault.jpg)