Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
5. Consciousness and Sleep
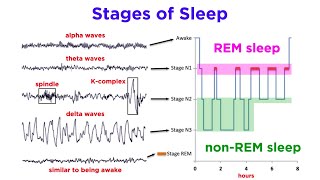
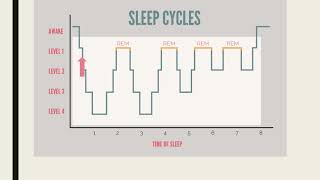
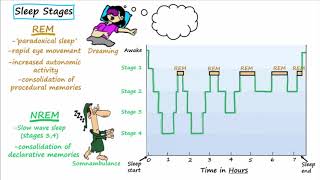
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Which structure or organ is thought to be responsible for stopping the eating response when glucose levels go up?
A
Pancreas
B
Stomach
C
Lateral hypothalamus
D
Ventromedial hypothalamus
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by understanding the role of glucose in the body. Glucose is a primary energy source, and its levels in the blood are tightly regulated.
Recognize that the brain plays a crucial role in monitoring and responding to changes in blood glucose levels.
Identify the hypothalamus as a critical brain region involved in regulating hunger and satiety. It contains several nuclei that respond to different physiological signals.
Differentiate between the lateral hypothalamus and the ventromedial hypothalamus. The lateral hypothalamus is associated with initiating eating, while the ventromedial hypothalamus is linked to stopping eating.
Conclude that the ventromedial hypothalamus is the structure responsible for stopping the eating response when glucose levels rise, as it signals satiety and fullness.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)