Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
1. Introduction to Psychology
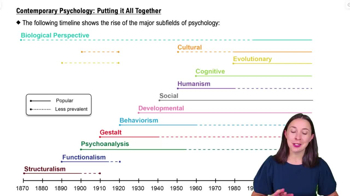
Contemporary Psychology: Putting it All Together
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
The theory of operant conditioning was developed by
A
John B. Watson.
B
Carl Rogers.
C
Abraham Maslow.
D
B. F. Skinner.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the context of operant conditioning: It is a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior.
Identify the key figure associated with operant conditioning: B. F. Skinner is the psychologist who developed this theory.
Differentiate operant conditioning from classical conditioning: Unlike classical conditioning, which involves associating an involuntary response and a stimulus, operant conditioning is about associating a voluntary behavior and a consequence.
Recognize the contributions of B. F. Skinner: He introduced concepts such as reinforcement and punishment to explain how behavior is acquired and maintained.
Review the other psychologists mentioned: John B. Watson is known for behaviorism, Carl Rogers for humanistic psychology, and Abraham Maslow for the hierarchy of needs, none of whom developed operant conditioning.

 4:54m
4:54mWatch next
Master Contemporary Psychology with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice