Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
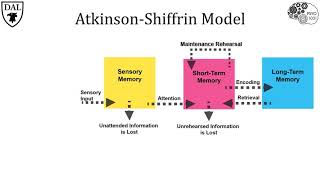
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Anterograde amnesia can be caused by
A
decay.
B
suggestion.
C
hypnosis.
D
a concussion.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of anterograde amnesia: It is a condition where an individual is unable to form new memories following the onset of the condition.
Identify the common causes of anterograde amnesia: These typically include physical brain injuries, such as concussions, which can disrupt the brain's ability to process and store new information.
Evaluate the options given: Decay, suggestion, and hypnosis are not typically associated with causing anterograde amnesia. Decay refers to the fading of memories over time, suggestion involves influencing someone's memory or perception, and hypnosis is a state of focused attention and increased suggestibility.
Recognize that a concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury that can lead to anterograde amnesia by damaging the brain regions responsible for memory formation.
Conclude that among the given options, a concussion is the most plausible cause of anterograde amnesia, as it directly affects the brain's ability to form new memories.

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)












































![The Girl With The Three-Minute Memory (Amnesia Documentary) | Real Stories [4k]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZeiMhUlipTk/mqdefault.jpg)