Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
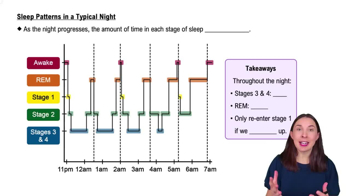
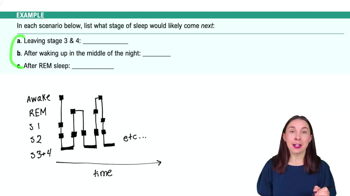
5. Consciousness and Sleep
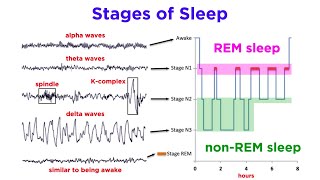
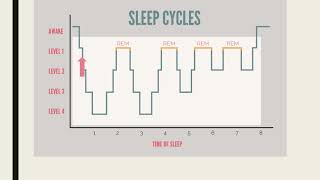
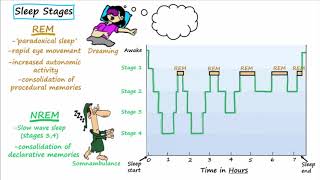
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
According to the James-Lange theory of emotion, a physiological response to a stimulus is caused by the arousal of the
A
sympathetic nervous system.
B
parasympathetic nervous system.
C
hypothalamus.
D
somatic nervous system.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the James-Lange theory of emotion, which posits that emotions are the result of physiological reactions to events.
Identify the role of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body's 'fight or flight' response, causing physiological arousal.
Consider the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for 'rest and digest' activities, typically reducing arousal.
Evaluate the function of the hypothalamus, which regulates various bodily functions but is not directly responsible for the physiological arousal described in the James-Lange theory.
Examine the somatic nervous system, which controls voluntary movements and is not primarily involved in the autonomic arousal process described by the James-Lange theory.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)