Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
6. Learning
Classical Conditioning
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
If your professor gives pop quizzes, this is an example of
A
a variable interval schedule of reinforcement.
B
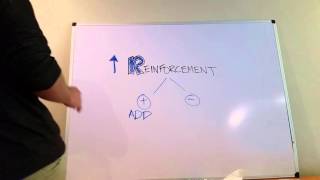
punishment by addition.
C
a fixed interval schedule of reinforcement.
D
a ratio schedule of reinforcement.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of reinforcement schedules: Reinforcement schedules are rules that determine how and when a behavior will be followed by a reinforcer. They are crucial in operant conditioning.
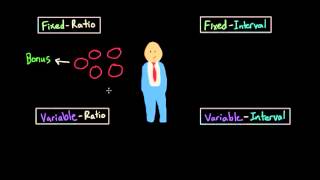
Identify the types of reinforcement schedules: There are four main types - fixed ratio, variable ratio, fixed interval, and variable interval. Each has distinct characteristics based on timing and frequency.
Define a variable interval schedule: In a variable interval schedule, reinforcement is given for the first response after a varying amount of time has passed. This schedule is unpredictable, which can lead to steady response rates.
Analyze the scenario: Pop quizzes are given at unpredictable times, which aligns with the concept of a variable interval schedule, as students cannot predict when the next quiz will occur.
Compare with other options: Fixed interval schedules have predictable timing, ratio schedules depend on the number of responses, and punishment by addition involves adding an unpleasant stimulus. These do not match the scenario of pop quizzes.

 3:29m
3:29mWatch next
Master Introduction to Classical Conditioning with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

















![Visual Illusions - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/7GJJXLiN4Ug/mqdefault.jpg)


























![Classical Conditioning [cc]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/cP5lCleK-PM/mqdefault.jpg)












































































































![3.22. Tardive Dystonia Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation - Dystonias [Spring Video Atlas]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ayPFIpXhoWY/mqdefault.jpg)