Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
4. Sensation and Perception
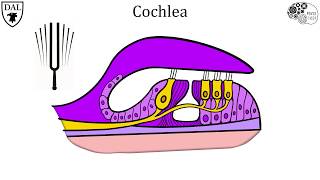
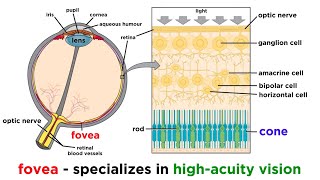
Visual Anatomy
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Motion sickness can be explained by
A
a type of allergic reaction.
B
conflict between visual input and other sensory input.
C
environmental discord.
D
an imbalance in the kinesthetic senses.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of motion sickness: Motion sickness occurs when there is a disconnect between the sensory inputs received by the brain, particularly between what the eyes see and what the inner ear senses.
Identify the key sensory systems involved: The visual system (eyes) and the vestibular system (inner ear) are primarily responsible for detecting motion and balance.
Recognize the conflict: Motion sickness often arises when there is a conflict between visual input (what you see) and vestibular input (what your inner ear senses). For example, reading a book in a moving car can cause motion sickness because your eyes are focused on a stationary object while your inner ear senses movement.
Consider the options: Evaluate each option provided in the problem. The correct explanation for motion sickness is the 'conflict between visual input and other sensory input,' as this aligns with the sensory mismatch theory.
Eliminate incorrect options: Discard options that do not align with the sensory conflict theory, such as 'a type of allergic reaction,' 'environmental discord,' and 'an imbalance in the kinesthetic senses,' as these do not accurately describe the cause of motion sickness.

 3:08m
3:08mWatch next
Master Anatomy of the Eye with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















![The Human Eye & Color Blindness [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 3] (3.3)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Mwq23JTBnN0/mqdefault.jpg)







![The Process Of Smelling & Tasting [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 6] (3.6)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/vIQf0QAJFQA/mqdefault.jpg)




![Sensation of Touch, Layers of Skin & Pain [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 7] (3.7)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/sjbg9pf9Cj8/mqdefault.jpg)























![Factors affecting perception - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ot4AjaQUo3Y/mqdefault.jpg)
![Social & Cognitive Factors In Learning [AP Psychology Unit 4 Topic 4] (4.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Z1NIcVXplFk/mqdefault.jpg)