Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
6. Learning
Classical Conditioning
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
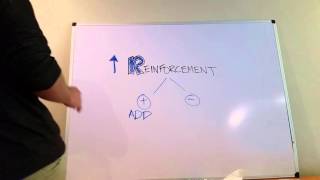
A teacher has decided to give 'caught being good' tickets to her students when they behave according to class rules. This teacher also rewards students with gold stars each time they improve their math speed. This teacher is using
A
punishment and classical conditioning.
B
operant conditioning.
C
observational learning.
D
classical conditioning.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the key components of the scenario: the teacher is giving 'caught being good' tickets and gold stars as rewards for specific behaviors.
Understand the concept of operant conditioning: it involves reinforcing desired behaviors through rewards or punishments.
Recognize that the teacher is using positive reinforcement by giving tickets and stars to encourage good behavior and improved math speed.
Differentiate between operant conditioning and classical conditioning: classical conditioning involves associating an involuntary response with a stimulus, while operant conditioning involves voluntary behaviors and consequences.
Conclude that the teacher's method aligns with operant conditioning, as it focuses on reinforcing voluntary behaviors with positive outcomes.

 3:29m
3:29mWatch next
Master Introduction to Classical Conditioning with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

















![Visual Illusions - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/7GJJXLiN4Ug/mqdefault.jpg)


























![Classical Conditioning [cc]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/cP5lCleK-PM/mqdefault.jpg)












































































































![3.22. Tardive Dystonia Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation - Dystonias [Spring Video Atlas]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ayPFIpXhoWY/mqdefault.jpg)