Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
2. Psychology Research
Intro to Research Methods
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
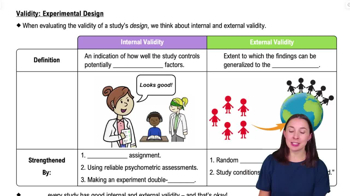
Why is random assignment an essential part of good experimental design?
A
Random assignment ensures that the sample accurately reflects the population.
B
It ensures that the experimental group will show the intended effects.
C
It increases equivalency between groups, reducing the odds of confounding variables affecting the results.
D
Random assignment ensures that the control group will not receive the independent variable.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the purpose of random assignment: It is used to distribute participants across different groups in an experiment in a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group.
Recognize the role of random assignment in increasing equivalency: By randomly assigning participants, researchers aim to create groups that are similar in all respects except for the treatment they receive, which helps in isolating the effect of the independent variable.
Identify how random assignment reduces confounding variables: Confounding variables are external factors that can affect the outcome of an experiment. Random assignment helps to minimize these variables by evenly distributing them across all groups.
Differentiate between random assignment and random sampling: Random assignment is about how participants are placed into groups, while random sampling is about how participants are selected from the population. Both are important but serve different purposes.
Consider the impact on experimental validity: By reducing the influence of confounding variables, random assignment enhances the internal validity of an experiment, making it more likely that the observed effects are due to the independent variable rather than other factors.

 1:46m
1:46mWatch next
Master Roadmap of the Lesson with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice