Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
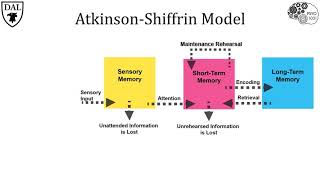
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Elvira knew the name of the first president of the United States without giving it a moment's thought. This is
A
nondeclarative (implicit) memory.
B
semantic memory.
C
episodic memory.
D
a retrieval cue.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the type of memory being described: Elvira knows the name of the first president of the United States without conscious effort.
Understand the concept of nondeclarative (implicit) memory: This type of memory involves skills and tasks that can be performed without conscious awareness, such as riding a bike or typing on a keyboard.
Recognize the concept of semantic memory: This is a type of declarative memory that involves facts and general knowledge about the world, such as knowing historical facts or the meaning of words.
Differentiate between episodic memory and semantic memory: Episodic memory involves personal experiences and specific events in time, while semantic memory involves general knowledge not tied to personal experience.
Consider the role of a retrieval cue: A retrieval cue is a stimulus that helps bring a memory to consciousness, but in this scenario, Elvira did not need a cue to recall the information.

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)












































![The Girl With The Three-Minute Memory (Amnesia Documentary) | Real Stories [4k]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZeiMhUlipTk/mqdefault.jpg)