Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
4. Sensation and Perception
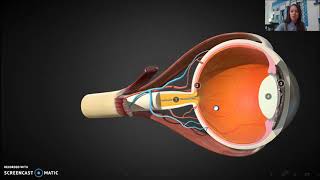
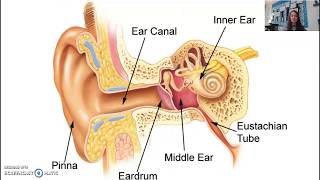
Visual Anatomy
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Which statement best explains how the sense of taste works?
A
Molecules of taste are absorbed into the saliva and circulated throughout the blood until they reach the brain.
B
Olfactory bulbs absorb molecules of taste and then send signals to the brain.
C
Molecules of food fit into receptors on taste buds, and neural signals are fired to the brain.
D
Molecules of taste are absorbed through receptors on the roof of the mouth and transmitted to the stomach.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by understanding the basic anatomy involved in the sense of taste. The primary structures are the taste buds, which are located on the tongue and contain taste receptor cells.
Recognize that taste perception involves the interaction between molecules of food and the taste receptors. These receptors are sensitive to different types of taste molecules, such as sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami.
When food molecules dissolve in saliva, they come into contact with the taste buds. The molecules bind to specific receptors on the taste receptor cells within the taste buds.
This binding action triggers a series of neural signals. These signals are transmitted via the gustatory pathway, which includes the cranial nerves, to the brain.
The brain processes these signals, allowing us to perceive and identify different tastes. This process is distinct from olfactory (smell) perception, which involves the olfactory bulbs and is not directly related to taste perception.

 3:08m
3:08mWatch next
Master Anatomy of the Eye with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















![The Human Eye & Color Blindness [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 3] (3.3)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Mwq23JTBnN0/mqdefault.jpg)







![The Process Of Smelling & Tasting [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 6] (3.6)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/vIQf0QAJFQA/mqdefault.jpg)




![Sensation of Touch, Layers of Skin & Pain [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 7] (3.7)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/sjbg9pf9Cj8/mqdefault.jpg)























![Factors affecting perception - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ot4AjaQUo3Y/mqdefault.jpg)
![Social & Cognitive Factors In Learning [AP Psychology Unit 4 Topic 4] (4.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Z1NIcVXplFk/mqdefault.jpg)