Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
3. Biological Psychology
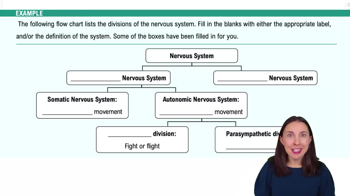
Organization of the Nervous System
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
The ________ system is likely active during a difficult exam while the _______ system is likely active while relaxing.
A
Central; peripheral.
B
Sympathetic; parasympathetic.
C
Autonomic; somatic.
D
Sympathetic; somatic.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the context: The question is about the body's response systems during different states of activity, specifically during stress and relaxation.
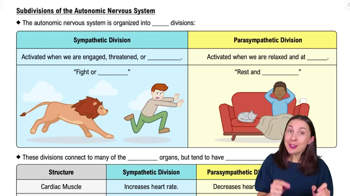
Identify the systems involved: The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is responsible for involuntary bodily functions and is divided into two main branches: the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
Recognize the role of the sympathetic system: This system is often referred to as the 'fight or flight' system. It is activated during stressful situations, such as taking a difficult exam, and prepares the body to respond to perceived threats by increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and inhibiting digestion.
Recognize the role of the parasympathetic system: This system is known as the 'rest and digest' system. It is active during relaxed states, promoting bodily functions that conserve energy, such as slowing the heart rate and stimulating digestion.
Match the systems to the scenarios: During a difficult exam, the sympathetic system is likely active, while during relaxation, the parasympathetic system is likely active.

 2:03m
2:03mWatch next
Master The Nervous System with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice