Table of contents
- 0. Fundamental Concepts of Algebra3h 29m
- 1. Equations and Inequalities3h 27m
- 2. Graphs1h 43m
- 3. Functions & Graphs2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 54m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Measuring Angles39m
- 8. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 9. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 10. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 11. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trig Equations1h 41m
- 12. Trigonometric Identities 2h 34m
- 13. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 14. Vectors2h 25m
- 15. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 16. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 17. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
- 18. Systems of Equations and Matrices1h 6m
- 19. Conic Sections2h 36m
- 20. Sequences, Series & Induction1h 15m
- 21. Combinatorics and Probability1h 45m
- 22. Limits & Continuity1h 49m
- 23. Intro to Derivatives & Area Under the Curve2h 9m
12. Trigonometric Identities
Introduction to Trigonometric Identities
Struggling with Precalculus?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
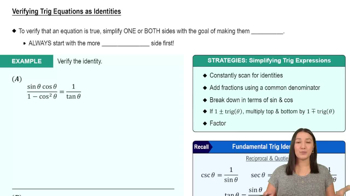
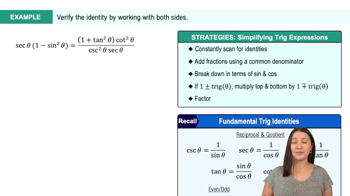
Identify the most helpful first step in verifying the identity.
(sin2θtan2θ−1)=sec2θsin2(−θ)
A
Add the terms on the left side using a common denominator.
B
Rewrite left side of equation in terms of sine and cosine.
C
Use even-odd identity to eliminate negative argument on right side of equation.
D
Rewrite right side of equation in terms of sine and cosine.

 6:19m
6:19mWatch next
Master Even and Odd Identities with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice