Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
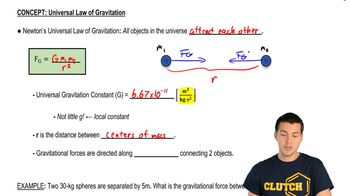
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation states that every mass attracts every other mass with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This law is fundamental for understanding gravitational interactions, such as the force between the sun and the comet in this scenario.
Recommended video:
Universal Law of Gravitation
Gravitational Acceleration
Gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of an object due to the gravitational force exerted by a massive body, such as the sun. It can be calculated using the formula a = F/m, where F is the gravitational force and m is the mass of the object experiencing the force. This concept is crucial for determining how quickly the comet is pulled toward the sun.
Recommended video:
Weight Force & Gravitational Acceleration
Distance in Gravitational Calculations
In gravitational calculations, the distance between the centers of two masses is critical, as it affects the gravitational force and acceleration. In this case, the distance of 75 million kilometers must be converted to meters for accurate calculations, as gravitational equations typically use SI units. Understanding how distance influences gravitational interactions is essential for solving the problem.
Recommended video:
Gravitational Forces in 2D
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance