Wave Functions definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackWave Functions definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
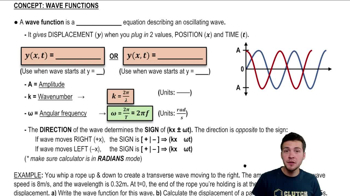
- Wave FunctionA sinusoidal equation describing the displacement of a particle on a string based on position and time.
- AmplitudeThe maximum displacement of a wave in either direction from its equilibrium position.
- Wave NumberA measure of spatial frequency of a wave, calculated as 2π divided by the wavelength.
- Angular FrequencyThe rate of change of the phase of a sinusoidal waveform, calculated as 2π times the frequency.
- Transverse WaveA wave in which particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
- Propagation VelocityThe speed at which the wave pattern moves through the medium.
- Transverse VelocityThe velocity of particles moving perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
- WavelengthThe distance between successive crests of a wave, often denoted by lambda (λ).
- FrequencyThe number of oscillations or cycles per unit time of a wave.
- Sine FunctionA mathematical function describing a smooth periodic oscillation, used in wave functions.
- Cosine FunctionA mathematical function similar to sine, used in wave functions to describe oscillations.
- RadiansA unit of angular measure used in wave functions, where 2π radians equals 360 degrees.
- Maximum Transverse VelocityThe product of angular frequency and amplitude, representing the peak speed of particle motion.
- PhaseThe position of a point in time on a waveform cycle, often expressed in terms of angle.
- DisplacementThe distance a particle moves from its equilibrium position in a wave.