Velocity in 2D definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackVelocity in 2D definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
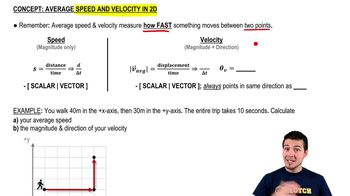
- SpeedA scalar quantity representing distance traveled over time, without direction.
- VelocityA vector quantity representing displacement over time, including both magnitude and direction.
- DisplacementA vector quantity representing the shortest path between two points, with both magnitude and direction.
- VectorA quantity with both magnitude and direction, used to represent displacement and velocity.
- ScalarA quantity with only magnitude, such as speed or distance, without direction.
- MagnitudeThe size or length of a vector, representing the amount without direction.
- DirectionThe orientation of a vector in space, often specified by an angle.
- ThetaThe angle used to describe the direction of a vector in two-dimensional motion.
- ComponentsThe projections of a vector along the axes, typically labeled as x and y components.
- VXThe x-component of a velocity vector, calculated using displacement or trigonometry.
- VYThe y-component of a velocity vector, calculated using displacement or trigonometry.
- Pythagorean TheoremA mathematical equation used to calculate the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
- Tangent InverseA trigonometric function used to calculate the angle of a vector from its components.
- HypotenuseThe longest side of a right triangle, opposite the right angle, representing the vector's magnitude.
- Trigonometric FunctionsMathematical functions like sine and cosine used to calculate vector components.