Intro to Cross Product (Vector Product) definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntro to Cross Product (Vector Product) definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
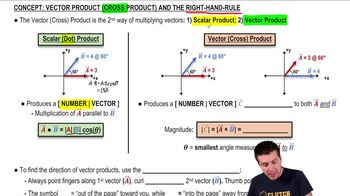
- Scalar ProductA method of vector multiplication resulting in a scalar, calculated using the cosine of the angle between vectors.
- Vector ProductA method of vector multiplication resulting in a new vector, perpendicular to the original vectors, using the sine of the angle.
- Right Hand RuleA technique to determine the direction of the vector product by pointing fingers along the first vector and curling towards the second.
- MagnitudeThe size or length of a vector, calculated for vector products using the sine of the angle between vectors.
- DirectionThe orientation of a vector in space, determined for vector products using the right hand rule.
- PerpendicularDescribes the relationship of the vector product to the original vectors, forming a right angle with them.
- Parallel ComponentsParts of a vector that lie in the same direction as another vector, used in scalar product calculations.
- AngleThe measure of rotation between two vectors, crucial for calculating both scalar and vector products.
- SineA trigonometric function used in calculating the magnitude of the vector product.
- CosineA trigonometric function used in calculating the scalar product of vectors.
- Zero Cross ProductOccurs when vectors are parallel or antiparallel, resulting in no vector product.
- 2D OrientationA plane in which vectors lie, affecting the calculation of vector products.
- 3D OrientationA spatial arrangement of vectors, requiring consideration of all three axes for vector products.
- Circle with DotA symbol indicating a vector pointing out of the page towards the observer.
- Circle with XA symbol indicating a vector pointing into the page away from the observer.