The Electromagnetic Spectrum definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackThe Electromagnetic Spectrum definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
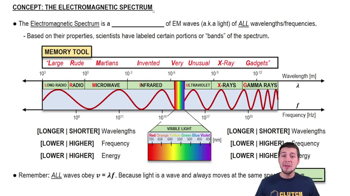
- Electromagnetic SpectrumA continuum of all electromagnetic waves, ranging from radio waves to gamma rays, with varying wavelengths and frequencies.
- WavelengthThe distance between successive crests of a wave, inversely proportional to frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum.
- FrequencyThe number of wave cycles per second, inversely proportional to wavelength and directly proportional to energy.
- Radio WavesThe longest wavelength electromagnetic waves, used for AM and FM radio transmissions.
- MicrowavesElectromagnetic waves with wavelengths shorter than radio waves, used in microwave ovens and radar technology.
- Infrared RadiationElectromagnetic waves perceived as heat, with wavelengths longer than visible light but shorter than microwaves.
- Visible LightThe portion of the electromagnetic spectrum visible to the human eye, encompassing all colors of the rainbow.
- Ultraviolet RaysElectromagnetic waves with wavelengths shorter than visible light, responsible for sunburns.
- X-raysHigh-energy electromagnetic waves used in medical imaging, with wavelengths shorter than ultraviolet rays.
- Gamma RaysThe shortest wavelength, highest energy electromagnetic waves, used in cancer treatment and emitted by cosmic sources.
- Speed of LightA constant speed at which light travels in a vacuum, approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second.
- EnergyDirectly proportional to frequency in electromagnetic waves, with higher frequencies having higher energy.
- ContinuumA continuous sequence or range, such as the electromagnetic spectrum, with no distinct boundaries.
- NanometerA unit of length equal to one billionth of a meter, used to measure wavelengths of light.
- MicrometerA unit of length equal to one millionth of a meter, used to measure wavelengths in the infrared spectrum.