The Doppler Effect of Light definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackThe Doppler Effect of Light definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
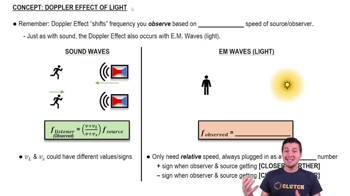
- Doppler EffectA phenomenon causing a shift in observed frequency due to relative motion between source and observer.
- Electromagnetic WavesWaves of electric and magnetic fields, including light, that can travel through a vacuum.
- FrequencyThe number of wave cycles that pass a point per unit time, measured in Hertz.
- WavelengthThe distance between successive crests of a wave, often measured in nanometers for light.
- Relative VelocityThe combined speed of the source and observer, used in calculating frequency shifts.
- Speed of LightA constant value of approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second, denoted as 'c'.
- Observed FrequencyThe frequency detected by an observer, altered by the Doppler effect.
- Source FrequencyThe original frequency emitted by a source before any Doppler shift.
- RecedingThe motion of a source moving away from an observer, causing a frequency decrease.
- ApproachingThe motion of a source moving towards an observer, causing a frequency increase.
- NanometerA unit of length equal to one billionth of a meter, often used to measure light wavelengths.
- HertzThe unit of frequency, equivalent to one cycle per second.
- LambdaA symbol commonly used to represent wavelength in equations.
- VelocityThe speed of something in a given direction, crucial in Doppler effect calculations.
- Light BulbAn example used to illustrate the Doppler effect with electromagnetic waves.