Standing Wave Functions definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackStanding Wave Functions definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Standing WaveA wave pattern formed by the interference of two waves traveling in opposite directions.
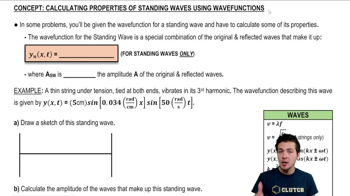
- Wave FunctionA mathematical description of a wave, often expressed as y(x, t) = ASW * sin(kx) * sin(ωt).
- AmplitudeThe maximum displacement of a wave from its rest position, doubled in standing waves.
- HarmonicA specific frequency at which a system naturally oscillates, denoted by n.
- NodeA point along a standing wave where the wave has minimal amplitude.
- AntinodeA point where the amplitude of a standing wave is at its maximum.
- Wave NumberA value denoted by k, related to the wavelength by k = 2π/λ.
- WavelengthThe distance between consecutive points of a wave in phase, calculated as λ = 2π/k.
- Angular FrequencyA measure of how many radians a wave oscillates per second, denoted by ω.
- PeriodThe time taken for one complete cycle of a wave, calculated as T = 2π/ω.
- InterferenceThe process by which two waves superpose to form a resultant wave.
- LoopA segment of a standing wave between two nodes, related to the harmonic number.
- String LengthThe length of the medium supporting the wave, calculated using L = n * λn / 2.
- RadiansA unit of angular measure used in the context of angular frequency.
- OscillationThe repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value.