Springs & Elastic Potential Energy definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackSprings & Elastic Potential Energy definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
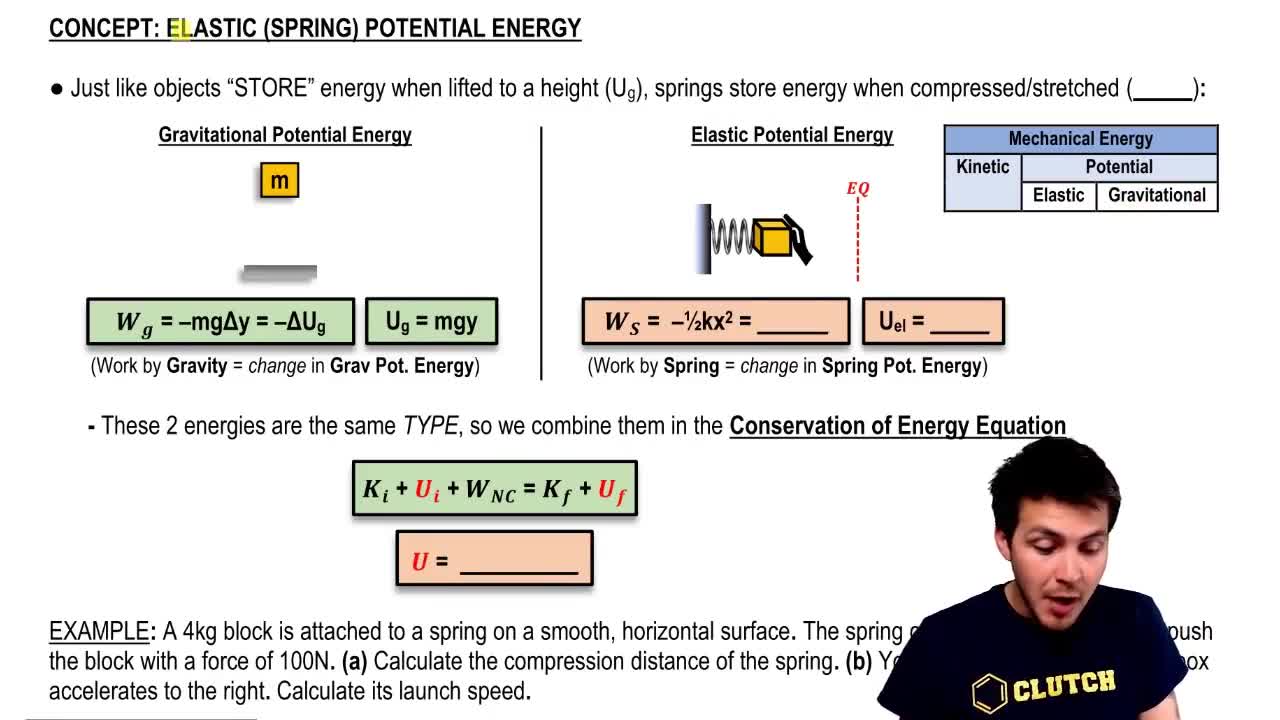
- Elastic Potential EnergyEnergy stored in a spring when compressed or stretched, calculated as 1/2kx^2.
- Spring ConstantA measure of a spring's stiffness, denoted as k, used in calculating elastic potential energy.
- DeformationThe change in length of a spring from its equilibrium position, denoted as x.
- Hooke's LawThe principle stating that the force exerted by a spring is proportional to its deformation.
- Equilibrium PositionThe natural length of a spring where no external forces are applied, resulting in zero stored energy.
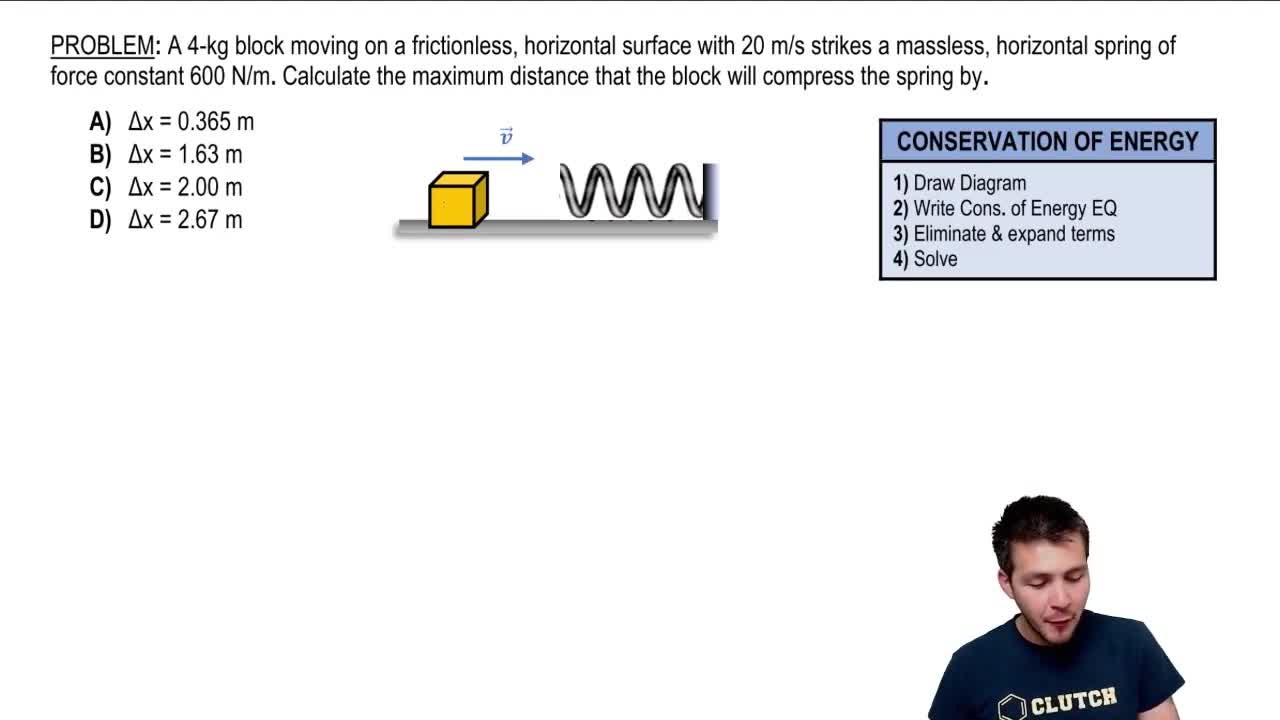
- Compression DistanceThe amount by which a spring is compressed from its equilibrium position.
- Launch SpeedThe velocity of an object released from a compressed or stretched spring.
- Kinetic EnergyThe energy of an object due to its motion, calculated as 1/2mv^2.
- Gravitational Potential EnergyEnergy stored due to an object's position in a gravitational field, calculated as mgy.
- Energy ConservationThe principle stating that total energy remains constant, combining kinetic and potential energies.
- Nonconservative ForcesForces like friction that cause energy dissipation, not conserved in mechanical energy equations.
- Applied ForceAn external force exerted on an object, such as pushing a block against a spring.
- Spring ForceThe force exerted by a spring, opposing deformation, calculated using Hooke's Law.
- Equilibrium DistanceThe distance at which a spring returns to its natural length after being deformed.
- Potential EnergyStored energy in a system due to its position or configuration, such as in springs or gravity.