Phase Diagrams, Triple Points and Critical Points definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPhase Diagrams, Triple Points and Critical Points definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
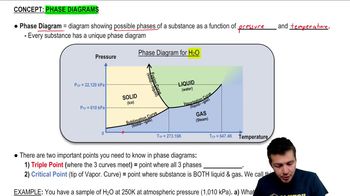
- Phase DiagramA graphical representation showing the phases of a substance as a function of pressure and temperature.
- Fusion CurveThe boundary on a phase diagram where solid and liquid phases coexist and transition.
- Vaporization CurveThe boundary on a phase diagram where liquid and gas phases coexist and transition.
- Sublimation CurveThe boundary on a phase diagram where solid and gas phases coexist and transition directly.
- Triple PointA unique point on a phase diagram where solid, liquid, and gas phases coexist in equilibrium.
- Critical PointThe endpoint of the vaporization curve where liquid and gas phases become indistinguishable.
- SolidA phase characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes in shape or volume.
- LiquidA phase with a definite volume but no fixed shape, adapting to the shape of its container.
- GasA phase with no fixed shape or volume, expanding to fill its container completely.
- PressureThe force exerted per unit area, influencing phase changes in a phase diagram.
- TemperatureA measure of thermal energy, determining the phase of a substance in a phase diagram.
- FluidA state where the distinction between liquid and gas phases disappears, occurring beyond the critical point.
- MeltingThe phase change from solid to liquid, occurring along the fusion curve.
- BoilingThe phase change from liquid to gas, occurring along the vaporization curve.
- SublimationThe phase change from solid directly to gas, occurring along the sublimation curve.