Parallel Plate Capacitors definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackParallel Plate Capacitors definitions
1/12
Terms in this set (12)
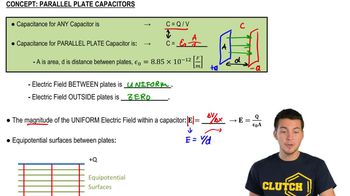
- Parallel Plate CapacitorA device with two plates of equal and opposite charges separated by a distance, used to store electrical energy.
- CapacitanceThe ability of a capacitor to store charge per unit voltage, calculated as C = (epsilon_0 * A) / d.
- Vacuum PermittivityA constant denoted as epsilon_0, representing the ability of a vacuum to permit electric field lines.
- Electric FieldA uniform field between capacitor plates, calculated as E = Q / (epsilon_0 * A), indicating force per unit charge.
- Equipotential SurfacesSurfaces between capacitor plates where potential is constant and perpendicular to electric field lines.
- ChargeThe quantity of electricity held by a capacitor, calculated as the product of capacitance and voltage.
- VoltageThe potential difference between capacitor plates, influencing the electric field and charge storage.
- AreaThe surface size of capacitor plates, affecting capacitance and electric field strength.
- DistanceThe separation between capacitor plates, inversely affecting capacitance and electric field.
- Gauss's LawA principle relating electric fields to charge distribution, explaining uniform fields in capacitors.
- FaradThe unit of capacitance, representing the capacity to store one coulomb per volt.
- Newton per CoulombThe unit of electric field strength, indicating force exerted per unit charge.