Newton's Law of Gravity definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackNewton's Law of Gravity definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
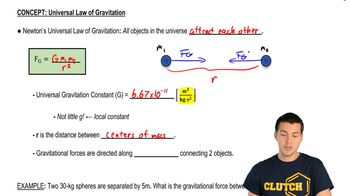
- Universal Law of GravitationA principle stating that every object attracts every other object with a force proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- Gravitational ConstantA universal constant denoted by G, valued at 6.67 x 10^-11 N(m/kg)^2, used in the calculation of gravitational forces.
- Local Gravitational ConstantThe acceleration due to gravity on Earth, approximately 9.8 m/s^2, differing from the universal gravitational constant.
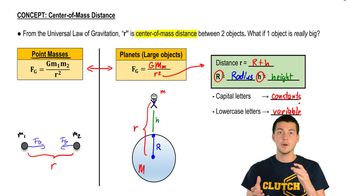
- Point MassAn object treated as if all its mass is concentrated at a single point, simplifying gravitational calculations.
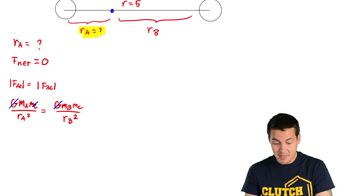
- Center of MassThe point in an object or system where the total mass can be considered to be concentrated for gravitational calculations.
- RadiusThe distance from the center of a sphere, like Earth, to its surface, used in gravitational calculations.
- HeightThe distance above a planet's surface, added to the radius to calculate the total distance in gravitational equations.
- NewtonThe unit of force in the International System of Units (SI), symbolized as N, used to measure gravitational force.
- MassA measure of the amount of matter in an object, influencing the gravitational force it exerts and experiences.
- DistanceThe separation between the centers of mass of two objects, crucial in calculating gravitational force.
- Action-ReactionNewton's third law principle stating that forces between two objects are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
- Order of OperationsA mathematical rule dictating the sequence in which operations are performed, crucial in solving equations accurately.
- VariableA symbol representing a quantity that can change, such as height in gravitational calculations.
- ConstantA fixed value that does not change, such as the gravitational constant or Earth's radius in calculations.
- EquationA mathematical statement that expresses the equality of two expressions, used to calculate gravitational forces.