More Conservation of Energy Problems definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackMore Conservation of Energy Problems definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
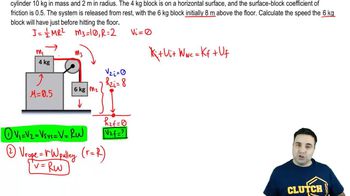
- PulleyA solid cylinder used to change the direction of a force applied via a rope or cable.
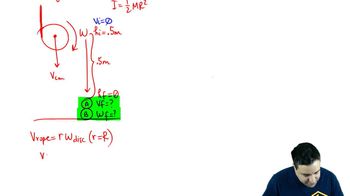
- Moment of InertiaA measure of an object's resistance to changes in its rotation, calculated as half the mass times the radius squared for a solid cylinder.
- Coefficient of FrictionA dimensionless scalar value representing the frictional force between two bodies in contact, here given as 0.5.
- Kinetic EnergyThe energy possessed by an object due to its motion, calculated as half the mass times velocity squared.
- Potential EnergyThe energy held by an object due to its position relative to other objects, calculated as mass times gravity times height.
- Conservation of EnergyA principle stating that the total energy in an isolated system remains constant, accounting for kinetic, potential, and work done by non-conservative forces.
- Rotational MotionThe motion of an object around a center or axis, contributing to kinetic energy in systems with pulleys.
- Linear VelocityThe rate of change of position of an object along a straight path, equal for all parts of the system in this problem.
- Angular VelocityThe rate of change of angular position of a rotating body, related to linear velocity by the radius of rotation.
- Work Done by FrictionThe energy transferred by the force of friction over a distance, calculated as the product of frictional force and distance.
- Normal ForceThe force perpendicular to the contact surface, equal to gravitational force for the 4 kg block on a horizontal surface.
- Gravitational ForceThe force of attraction between an object and the Earth, calculated as mass times the acceleration due to gravity.
- Solid CylinderA three-dimensional geometric shape with a circular base and a specific height, used to model the pulley.
- SystemA group of interacting or interrelated entities that form a unified whole, such as the blocks and pulley in this problem.
- ExpressionA mathematical phrase derived to represent the final velocity of the block, involving algebraic manipulation of energy equations.