Mass Distribution with Calculus definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackMass Distribution with Calculus definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
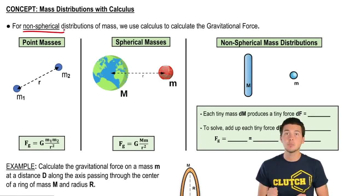
- Gravitational ForceThe force of attraction between two masses, calculated using Newton's law of gravity.
- Non-spherical Mass DistributionA mass configuration that cannot be approximated as a point mass at its center.
- Differential Mass (DM)A small segment of mass used in calculus to approximate a continuous mass distribution.
- Differential Force (DF)The infinitesimal force generated by a differential mass in a gravitational field.
- IntegralA mathematical operation used to sum infinitesimal quantities, such as forces or masses.
- Center of Mass DistanceThe distance from a point mass to the center of mass of a distribution.
- Vector DecompositionThe process of breaking a vector into its component parts, typically along orthogonal axes.
- CosineA trigonometric function representing the adjacent side over the hypotenuse in a right triangle.
- HypotenuseThe longest side of a right triangle, opposite the right angle.
- Pythagorean TheoremA mathematical relation in a right triangle: the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
- ConstantsValues that do not change during the integration process, such as G and M in gravitational calculations.
- Radius of the RingThe fixed distance from the center to any point on the circumference of a ring.
- Distance (D)The horizontal distance from a point mass to the center of a mass distribution.
- Three Halves PowerAn exponent indicating a value raised to the power of 1.5, often seen in gravitational formulas.
- Mass (M)The total amount of matter in an object, often used as a constant in gravitational equations.