Kepler's Third Law for Elliptical Orbits definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackKepler's Third Law for Elliptical Orbits definitions
1/10
Terms in this set (10)
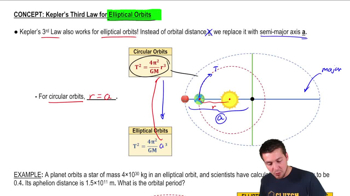
- Elliptical OrbitsPaths of celestial objects that are oval-shaped, with varying distances from the central body.
- Semi-Major AxisHalf the longest diameter of an ellipse, crucial for calculating orbital periods in elliptical orbits.
- Aphelion DistanceThe farthest point in an orbit from the central body, used to calculate the semi-major axis.
- EccentricityA measure of how much an orbit deviates from being circular, affecting the shape of the orbit.
- Orbital PeriodThe time taken for a celestial object to complete one full orbit around another object.
- Gravitational ConstantA fundamental constant (G) used in the calculation of gravitational forces and orbital dynamics.
- Mass of Central BodyThe mass of the object being orbited, crucial for determining the orbital period using Kepler's laws.
- Circular OrbitsA special case of elliptical orbits where the path is a perfect circle, with constant distance from the center.
- Perihelion DistanceThe closest point in an orbit to the central body, not used in the given example calculation.
- Kepler's Third LawA law relating the square of the orbital period to the cube of the semi-major axis of an orbit.