Refrigerators definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackRefrigerators definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
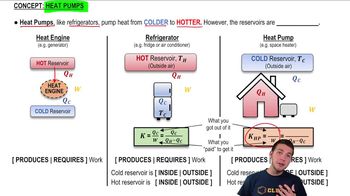
- RefrigeratorA device that transfers heat from a cold reservoir to a hot reservoir using work input.
- Heat EngineA system that converts heat energy into work by taking heat from a hot reservoir and expelling waste heat to a cold reservoir.
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsA principle stating that heat cannot spontaneously flow from a colder body to a hotter body without work input.
- Coefficient of Performance (COP)A measure of a refrigerator's efficiency, calculated as the heat removed from the cold reservoir divided by the work input.
- Cyclic ProcessA process in which a system returns to its initial state, resulting in no change in internal energy.
- Cold ReservoirThe part of a refrigerator or heat pump from which heat is extracted.
- Hot ReservoirThe part of a refrigerator or heat pump to which heat is expelled.
- WorkThe energy required to transfer heat from a cold reservoir to a hot reservoir in a refrigerator.
- Heat PumpA device similar to a refrigerator that transfers heat from a cold outside environment to a warmer interior space.
- Clausius StatementA formulation of the second law of thermodynamics stating that heat cannot flow from cold to hot without work.
- EfficiencyA measure of how well a heat engine converts heat into work, expressed as the ratio of work output to heat input.
- PowerThe rate at which work is done or energy is transferred, measured in watts.
- JouleA unit of energy or work in the International System of Units, equivalent to one watt-second.
- KilojouleA unit of energy equal to 1,000 joules, often used to express energy quantities in thermodynamics.
- Energy Flow DiagramA visual representation of the energy transfers and transformations in a system, such as a refrigerator or heat pump.