Heat Engines and the Second Law of Thermodynamics definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackHeat Engines and the Second Law of Thermodynamics definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
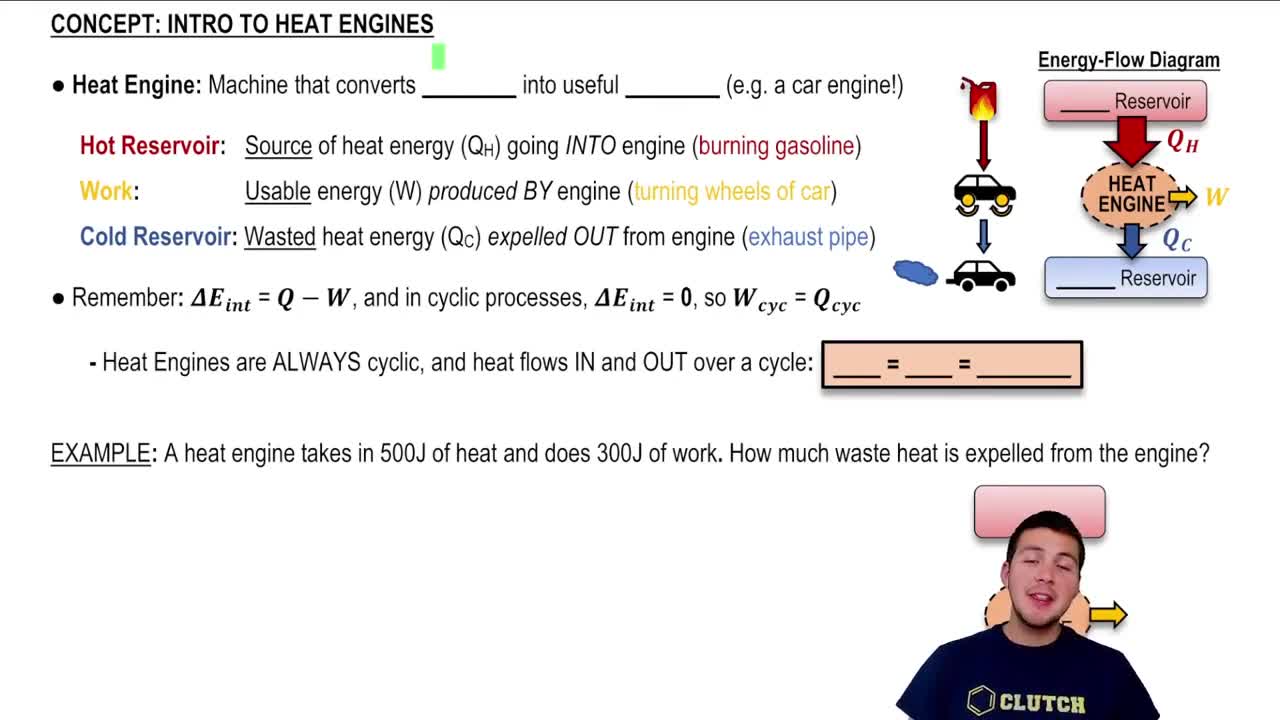
- Heat EngineA device that converts heat energy into useful work through a cyclic process.
- Hot ReservoirThe source of heat energy entering a heat engine, such as burning gasoline.
- Cold ReservoirThe destination for waste heat expelled from a heat engine.
- Energy Flow DiagramA representation of heat transfers in a heat engine, showing hot and cold reservoirs.
- Cyclic ProcessA repeating sequence in a heat engine where heat is converted to work and waste heat is expelled.
- Thermal EfficiencyA measure of how effectively a heat engine converts heat into work, expressed as a ratio.
- First Law of ThermodynamicsStates that the change in internal energy equals heat added minus work done.
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsStates that no heat engine can convert all input heat into work without waste heat.
- Perpetual Motion MachineA hypothetical machine that can operate indefinitely without an energy source, deemed impossible.
- WorkThe usable energy produced by a heat engine, such as turning car wheels.
- Waste HeatThe portion of heat energy not converted to work and expelled to the cold reservoir.
- Efficiency EquationThe formula for efficiency, expressed as work output divided by heat input.
- Kelvin StatementA principle of the second law of thermodynamics stating 100% efficiency is impossible.
- QHSymbol representing the heat input into a heat engine from the hot reservoir.
- QCSymbol representing the waste heat expelled to the cold reservoir.