Intro to Electromagnetic (EM) Waves definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntro to Electromagnetic (EM) Waves definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
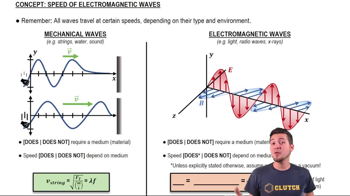
- Electromagnetic WavesWaves consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, perpendicular to each other, traveling through space without a medium.
- Electric FieldA field around charged particles that exerts force on other charges, oscillating in electromagnetic waves.
- Magnetic FieldA field produced by moving electric charges, oscillating perpendicular to the electric field in electromagnetic waves.
- Right-Hand RuleA method to determine the direction of electromagnetic wave travel using hand orientation with electric and magnetic fields.
- Speed of LightThe constant speed at which electromagnetic waves travel in a vacuum, approximately 3.0 x 10^8 meters per second.
- VacuumA space devoid of matter where electromagnetic waves can travel without a medium.
- PerpendicularDescribes the orientation of electric and magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves, forming right angles to each other.
- OscillationThe repetitive variation, typically in time, of the magnitude and direction of electric and magnetic fields in waves.
- MagnitudeThe strength or size of the electric or magnetic field in an electromagnetic wave.
- DirectionThe path along which electromagnetic waves travel, determined by the right-hand rule.
- MediumA substance through which mechanical waves travel, not required for electromagnetic waves.
- Mechanical WavesWaves that require a medium to travel, such as sound or water waves, unlike electromagnetic waves.
- PermittivityA measure of how an electric field affects and is affected by a dielectric medium, relevant in electromagnetic theory.
- PermeabilityA measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself.
- TeslaThe unit of magnetic field strength in the International System of Units (SI).