How Dielectrics Work definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackHow Dielectrics Work definitions
1/10
Terms in this set (10)
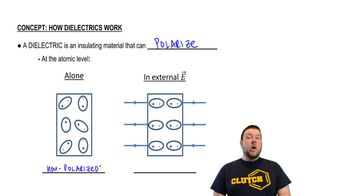
- DielectricAn insulating material capable of polarizing in response to an external electric field.
- PolarizationThe alignment of charges within a material in response to an external electric field.
- InsulatorA material that does not conduct electricity and can polarize when exposed to an electric field.
- Electric FieldA field around charged particles that exerts a force on other charges, influencing their alignment.
- CapacitorA device that stores electrical energy in an electric field, affected by the presence of a dielectric.
- Charge AlignmentThe orientation of positive and negative charges in a dielectric under an electric field.
- Field LinesImaginary lines representing the direction and strength of an electric field.
- VacuumA space devoid of matter, where electric field lines are not absorbed by any material.
- Atomic LevelThe scale at which individual atoms and their interactions are considered.
- Field ReductionThe decrease in electric field strength within a dielectric compared to a vacuum.