Heat Equations for Special Processes & Molar Specific Heats definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackHeat Equations for Special Processes & Molar Specific Heats definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
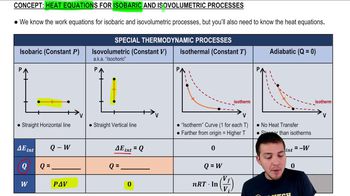
- Isobaric ProcessA thermodynamic process occurring at constant pressure, often involving work done by or on the system.
- Isovolumetric ProcessA thermodynamic process occurring at constant volume, where no work is done by the system.
- Molar Specific HeatThe amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance by one degree Celsius.
- C_PMolar specific heat at constant pressure, used in isobaric processes.
- C_VMolar specific heat at constant volume, used in isovolumetric processes.
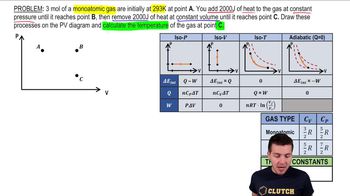
- Monoatomic GasA gas consisting of single atoms, with specific heat values of 3/2 R for C_V and 5/2 R for C_P.
- Diatomic GasA gas consisting of molecules with two atoms, with specific heat values of 5/2 R for C_V and 7/2 R for C_P.
- Internal EnergyThe total energy contained within a system, including kinetic and potential energy of particles.
- Heat TransferThe process of energy transfer from one body or system to another due to temperature difference.
- PV DiagramA graphical representation of the pressure-volume relationship in a thermodynamic process.
- First Law of ThermodynamicsEnergy conservation principle stating that the change in internal energy equals heat added minus work done.
- R (Gas Constant)A constant used in equations of state for gases, approximately 8.314 J/(mol·K).
- IsothermA line on a PV diagram representing a process occurring at constant temperature.
- Delta TThe change in temperature, calculated as the final temperature minus the initial temperature.
- CalorimetryThe science of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes.