Gravitational Force Inside the Earth definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackGravitational Force Inside the Earth definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
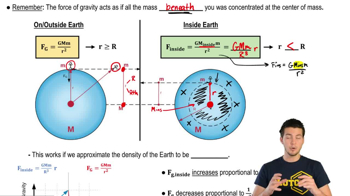
- Gravitational ForceThe force of attraction between two masses, calculated differently inside the Earth compared to its surface.
- DensityA measure of mass per unit volume, assumed constant for deriving gravitational force inside the Earth.
- Center of MassThe point where the mass of an object is concentrated, crucial for calculating gravitational force.
- Spherical ShellA hollow sphere used to conceptualize the mass distribution inside the Earth for gravitational calculations.
- VolumeThe amount of space occupied by an object, used in calculating the mass inside a smaller sphere of Earth.
- Newton's Law of GravityA law stating that every mass attracts every other mass with a force proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- Weightless ConditionA state at the Earth's center where gravitational force is zero due to symmetrical mass distribution.
- ProportionalA relationship where one quantity increases or decreases as another quantity does, such as gravitational force with distance inside Earth.
- RadiusThe distance from the center of a sphere to its surface, used in calculating gravitational force inside Earth.
- MassThe amount of matter in an object, crucial for calculating gravitational force both inside and outside the Earth.
- Surface WeightThe weight of an object measured at the Earth's surface, used as a reference for calculating weight inside the Earth.
- Gravitational AccelerationThe acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface, approximately 9.8 m/s², used to convert weight to mass.
- ConstantA value that does not change, such as the gravitational constant used in force calculations.
- Symmetrical DistributionAn even distribution of mass around a center point, leading to zero gravitational force at the Earth's center.
- Internal Gravitational Force FormulaA formula used to calculate gravitational force inside the Earth, involving mass and distance from the center.