Pressure Gauge: Manometer definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPressure Gauge: Manometer definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
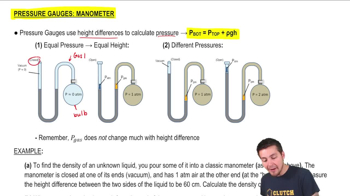
- ManometerA U-shaped tube used to measure pressure differences by comparing liquid column heights.
- Pressure GaugeAn instrument used to measure the pressure of gases or liquids.
- VacuumA space devoid of matter, resulting in zero pressure.
- AtmosphereA unit of pressure defined as 101,325 Pascals, equivalent to the pressure exerted by Earth's atmosphere at sea level.
- DensityThe mass per unit volume of a substance, often measured in kilograms per cubic meter.
- Height DifferenceThe vertical distance between liquid levels in a manometer, used to calculate pressure differences.
- PascalThe SI unit of pressure, equivalent to one newton per square meter.
- Gas ColumnA vertical section of gas in a manometer, assumed to have uniform pressure throughout.
- Pressure RatioThe proportional relationship between pressure changes and height changes in a manometer.
- Liquid ColumnThe vertical section of liquid in a manometer, where pressure varies with depth.
- P BottomThe pressure at the bottom of a liquid column in a manometer.
- P TopThe pressure at the top of a liquid column in a manometer.
- RhoThe symbol for density in the equation p_bottom = p_top + rho*g*h.
- GThe acceleration due to gravity, approximately 9.8 m/s², used in pressure calculations.
- BulbThe part of a manometer containing gas, affecting the pressure on one side of the liquid column.